Picking the right network cable can feel confusing. There are different types, like Cat 5, Cat 6, and Cat 7, and they all seem similar at first. If you have ever looked at the wires behind your router or tried to set up a home network, you might have wondered what these names mean and if they really matter. This post breaks down the basics of Ethernet cables, how they work, and what sets each type apart. You will learn about speed, how much data each cable can handle, how they look, and which one might be best for your home. If you want clear answers about Cat 5, Cat 6, and Cat 7 cables, keep reading.
What Are Ethernet Cables?
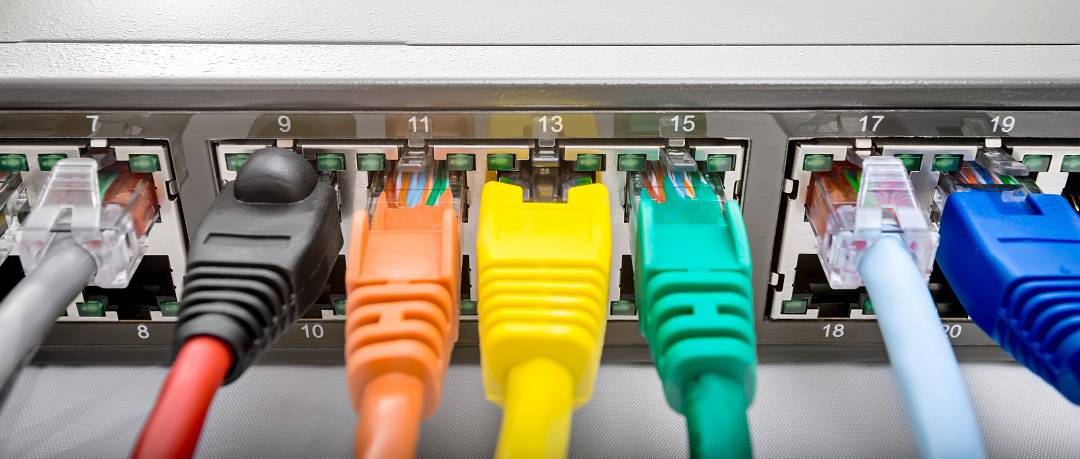
Ethernet cables are used to connect devices to a local area network. They move data using electrical signals, letting computers, printers, and other devices talk to each other. These cables are a common way to share files, use the internet, and connect to other services in homes and offices.
The physical look of Ethernet cables is pretty simple. They are round or flat cables, often with a plastic jacket, and usually come in colors like blue, yellow, or gray. Both ends of the cable have connectors called RJ45 plugs, which snap into ports on network devices. These plugs have metal contacts that line up with the wires inside the cable to make the connection work.
Cable quality can affect how well your network runs. Good cables have strong jackets and wires that can handle more data with fewer problems. Poor quality cables might cause dropped connections or slower speeds. Picking a cable that matches your needs helps keep your network stable and steady.
Cat 5, Cat 6, and Cat 7: Main Differences
Cat 5, Cat 6, and Cat 7 cables are used for wired networks, but they are different when it comes to speed and bandwidth. Cat 5 cables can handle speeds up to 100 Mbps and a bandwidth of up to 100 MHz. Cat 6 cables can reach speeds up to 1 Gbps with a bandwidth up to 250 MHz, and they can sometimes support 10 Gbps for short runs. Cat 7 cables are designed for higher speeds, going up to 10 Gbps with a bandwidth of 600 MHz.
Shielding is another area where these cables are not the same. Shielding protects the data signal from interference which can cause slow downs. Cat 5 cables usually do not have shielding, so they can pick up more interference from other electronic devices. Cat 6 cables sometimes have shielding, but not always. Cat 7 cables always have shielding around each pair of wires and around the whole cable. This helps keep out interference, which can be helpful in places with a lot of electronic noise.
Distance is the last main difference. Cat 5 and Cat 6 cables can send data up to 100 meters at their top speed, but Cat 6 can only handle its highest speeds for shorter distances, usually up to 55 meters for 10 Gbps. Cat 7 cables can go up to 100 meters for 10 Gbps connections. These differences matter most when you want to set up a network that needs high speed or will be running cables over long distances.
Choosing the Right Cable for Your Home Network
Before you pick a network cable, you might want to look at your internet speed, the devices you use, and how far the cable needs to reach. If you just need to connect a few devices for basic web browsing or streaming, you probably do not need the highest grade cable. You can also think about if you plan to upgrade your internet plan soon or add more connected devices. If you are running cable through walls or ceilings, it can be harder to replace, so picking a cable that will last for years can save time and money later.
Cat 5 cables are used mostly for older networks with slower speeds up to 100 Mbps. They’re perfect for web browsing and single device streaming. Cat 5e cables are more common for home networks and can handle speeds up to 1 Gbps, which works for most home internet plans. Cat 6 cables support up to 10 Gbps at short distances and are often picked for gaming, streaming in high definition, or for runs that have multiple computers connected to it like through a switch or router. Cat 6a cables can also handle 10 Gbps but work better for longer distances. Cat 7 cables are not used as much in homes, but some people use them for future-proofing or special cases where shielding from outside signals is needed.
In Summary
When it comes to picking between Cat 5, Cat 6, and Cat 7 network cables, it helps to match the cable to what you need for your home or office. Cat 5 works for slower speeds and older setups, while Cat 6 is a good choice for faster connections and most modern uses. If you want stronger shielding or plan to run cables in places with a lot of electronic noise, Cat 7 could make sense, but it is more than most people need. Looking at your internet plan, how many devices you have, and how far you need to run your cables can help you decide. Picking the right cable can help your network run better and save you trouble down the road.